Go to the source code of this file.
Macros | |
| #define | NAME_MAX 14 |
| Maximum length of a file name component. More... | |
Functions | |
| bool | dir_create (block_sector_t sector, size_t entry_cnt) |
| Opening and closing directories. More... | |
| struct dir * | dir_open (struct inode *) |
| Opens and returns the directory for the given INODE, of which it takes ownership. More... | |
| struct dir * | dir_open_root (void) |
| Opens the root directory and returns a directory for it. More... | |
| struct dir * | dir_reopen (struct dir *) |
| Opens and returns a new directory for the same inode as DIR. More... | |
| void | dir_close (struct dir *) |
| Destroys DIR and frees associated resources. More... | |
| struct inode * | dir_get_inode (struct dir *) |
| Returns the inode encapsulated by DIR. More... | |
| bool | dir_lookup (const struct dir *, const char *name, struct inode **) |
| Reading and writing. More... | |
| bool | dir_add (struct dir *, const char *name, block_sector_t) |
| Adds a file named NAME to DIR, which must not already contain a file by that name. More... | |
| bool | dir_remove (struct dir *, const char *name) |
| Removes any entry for NAME in DIR. More... | |
| bool | dir_readdir (struct dir *, char name[NAME_MAX+1]) |
| filesys/directory.h More... | |
Macro Definition Documentation
◆ NAME_MAX
| #define NAME_MAX 14 |
Maximum length of a file name component.
This is the traditional UNIX maximum length. After directories are implemented, this maximum length may be retained, but much longer full path names must be allowed.
Definition at line 12 of file directory.h.
Function Documentation
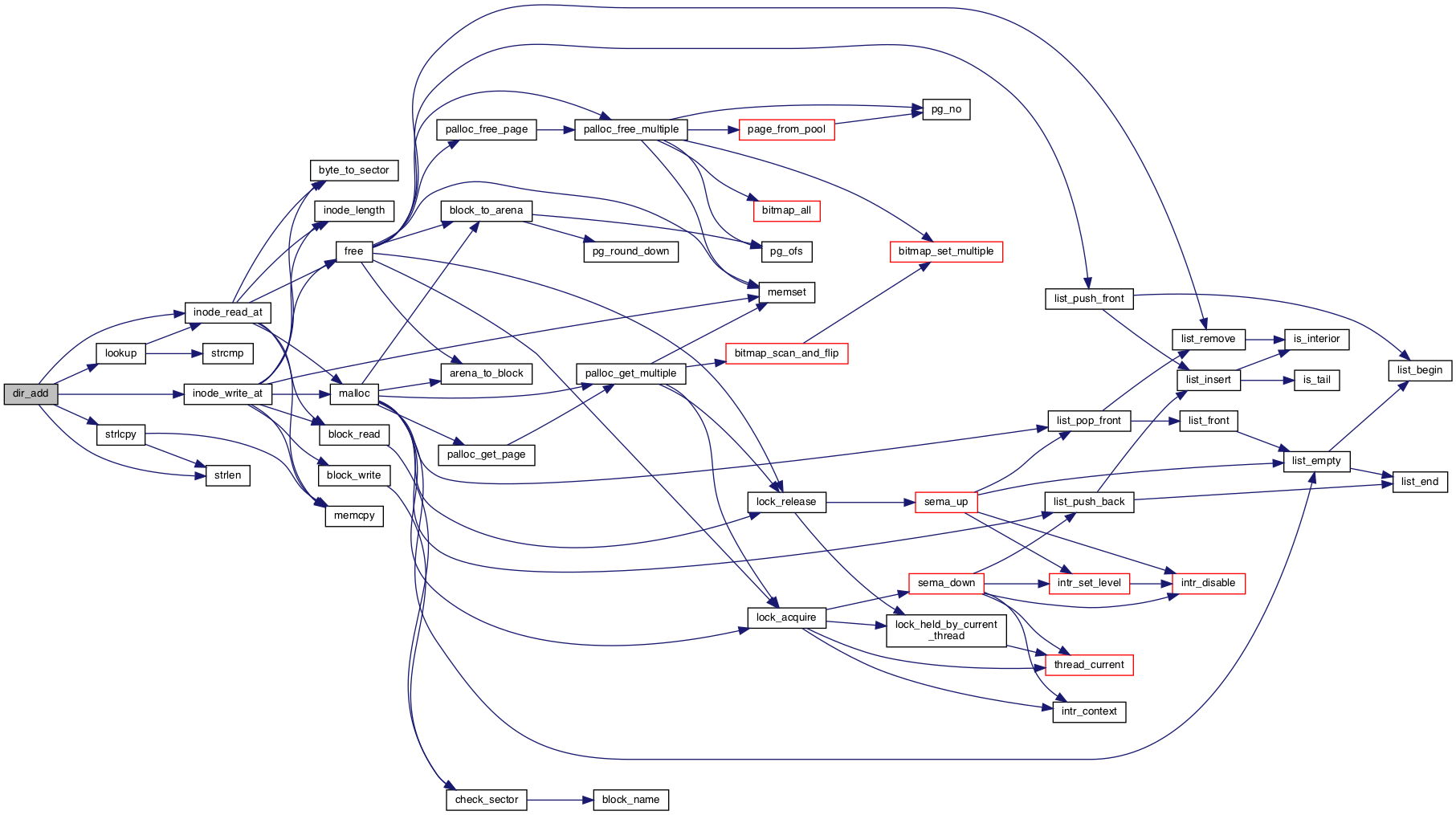
◆ dir_add()
| bool dir_add | ( | struct dir * | dir, |
| const char * | name, | ||
| block_sector_t | inode_sector | ||
| ) |
Adds a file named NAME to DIR, which must not already contain a file by that name.
The file's inode is in sector INODE_SECTOR. Returns true if successful, false on failure. Fails if NAME is invalid (i.e. too long) or a disk or memory error occurs.
Definition at line 142 of file directory.c.
References ASSERT, dir_entry::in_use, dir::inode, inode_read_at(), dir_entry::inode_sector, inode_write_at(), lookup(), name, dir_entry::name, NAME_MAX, NULL, strlcpy(), and strlen().
Referenced by filesys_create().
◆ dir_close()
| void dir_close | ( | struct dir * | dir | ) |
Destroys DIR and frees associated resources.
Definition at line 70 of file directory.c.
References free(), dir::inode, inode_close(), and NULL.
Referenced by filesys_create(), filesys_open(), filesys_remove(), and fsutil_ls().
◆ dir_create()
| bool dir_create | ( | block_sector_t | sector, |
| size_t | entry_cnt | ||
| ) |
Opening and closing directories.
Opening and closing directories.
Returns true if successful, false on failure.
Definition at line 27 of file directory.c.
References inode_create().
Referenced by do_format().

◆ dir_get_inode()
Returns the inode encapsulated by DIR.
Definition at line 81 of file directory.c.
References dir::inode.
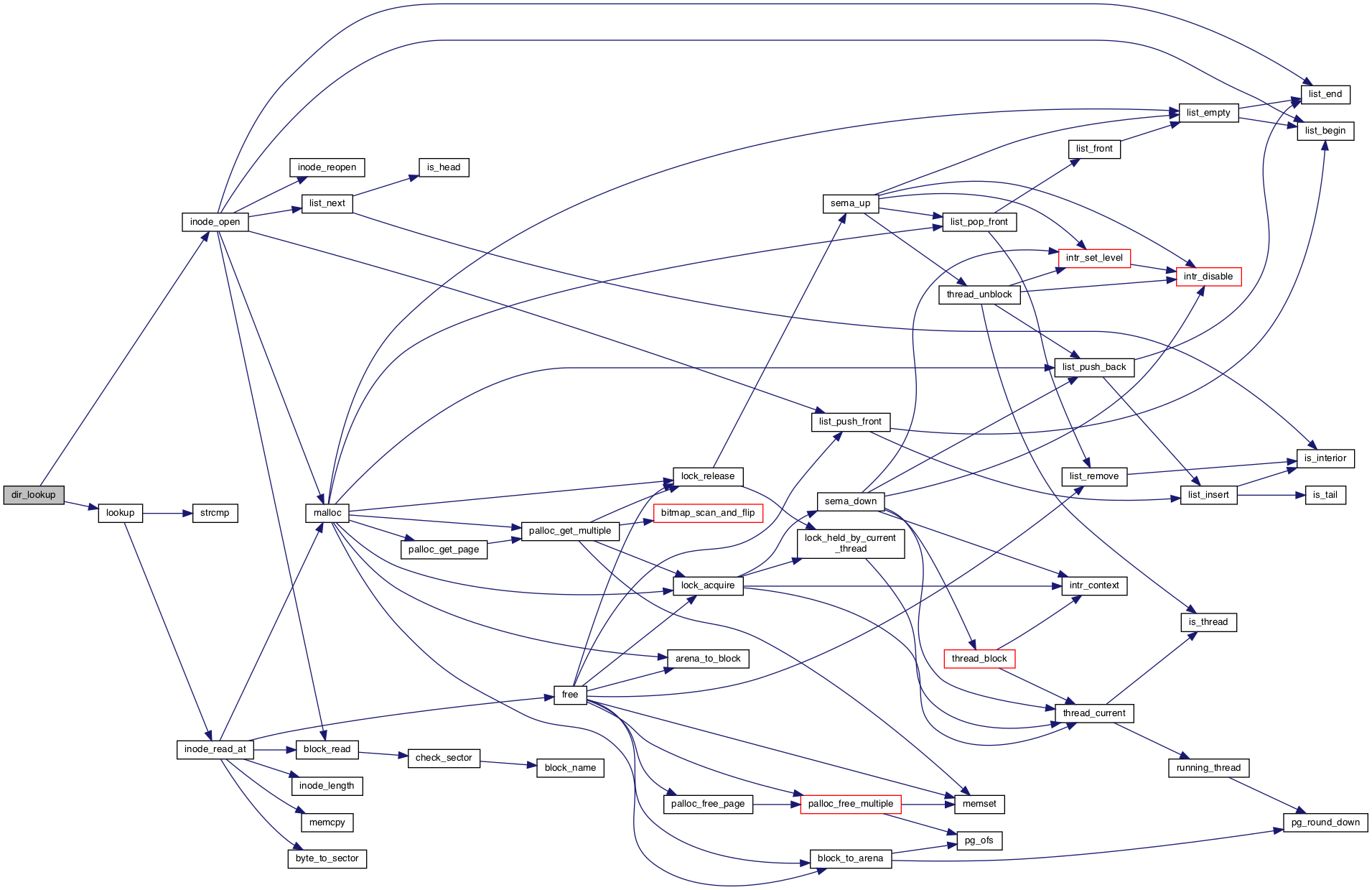
◆ dir_lookup()
Reading and writing.
Reading and writing.
On success, sets *INODE to an inode for the file, otherwise to a null pointer. The caller must close *INODE.
Definition at line 119 of file directory.c.
References ASSERT, inode_open(), dir_entry::inode_sector, lookup(), name, and NULL.
Referenced by filesys_open().
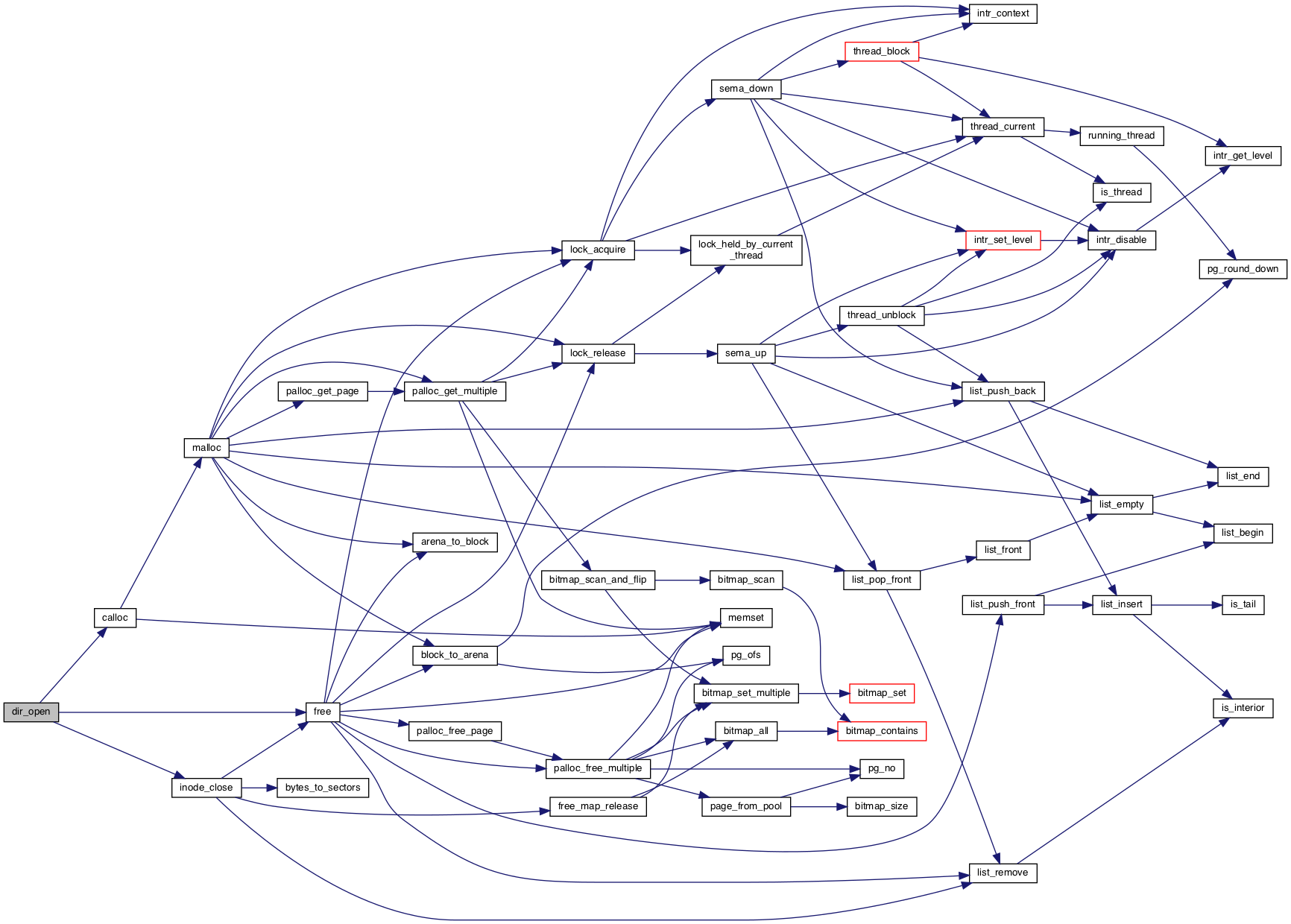
◆ dir_open()
Opens and returns the directory for the given INODE, of which it takes ownership.
Returns a null pointer on failure.
Definition at line 35 of file directory.c.
References calloc(), free(), dir::inode, inode_close(), NULL, and dir::pos.
Referenced by dir_open_root(), and dir_reopen().
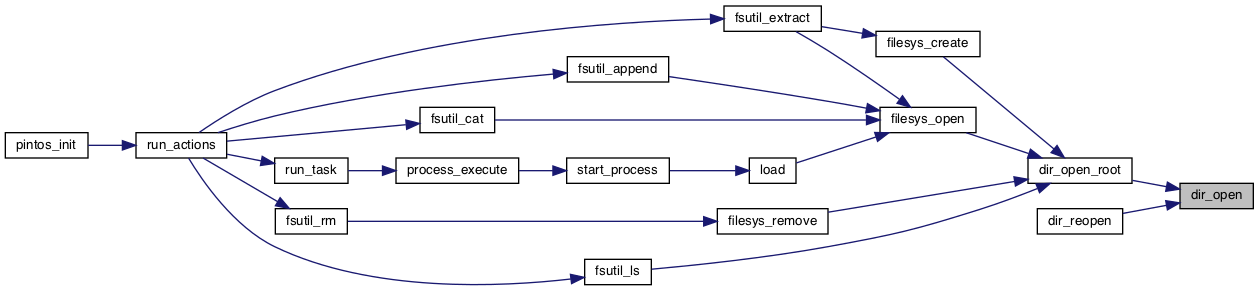
◆ dir_open_root()
| struct dir * dir_open_root | ( | void | ) |
Opens the root directory and returns a directory for it.
Return true if successful, false on failure.
Definition at line 55 of file directory.c.
References dir_open(), inode_open(), and ROOT_DIR_SECTOR.
Referenced by filesys_create(), filesys_open(), filesys_remove(), and fsutil_ls().
◆ dir_readdir()
Returns true if successful, false if the directory contains no more entries.
Definition at line 222 of file directory.c.
References dir_entry::in_use, dir::inode, inode_read_at(), name, dir_entry::name, NAME_MAX, dir::pos, and strlcpy().
Referenced by fsutil_ls().

◆ dir_remove()
Removes any entry for NAME in DIR.
Returns true if successful, false on failure, which occurs only if there is no file with the given NAME.
Definition at line 185 of file directory.c.
References ASSERT, dir_entry::in_use, dir::inode, inode_close(), inode_open(), inode_remove(), dir_entry::inode_sector, inode_write_at(), lookup(), name, and NULL.
Referenced by filesys_remove().
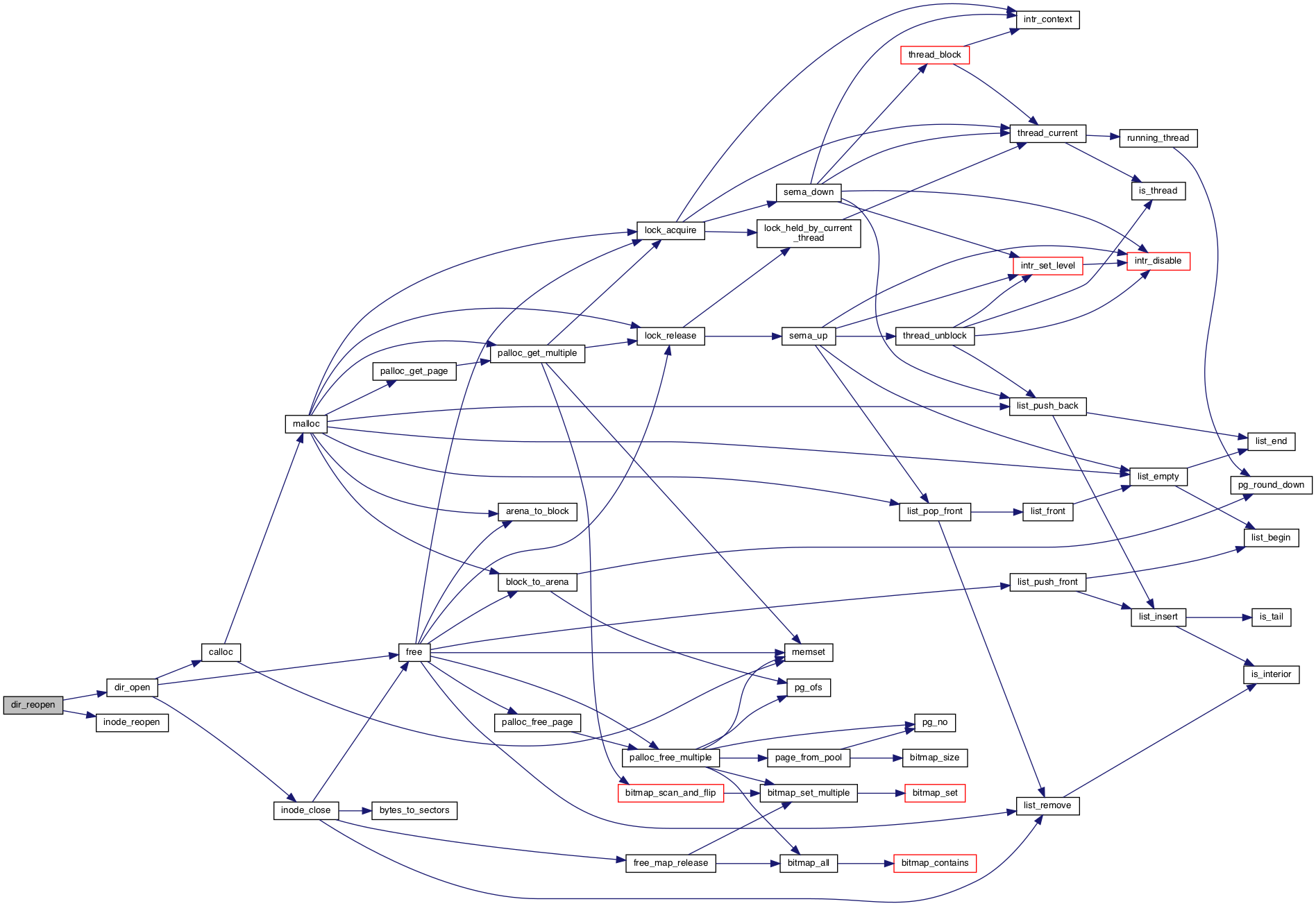
◆ dir_reopen()
Opens and returns a new directory for the same inode as DIR.
Returns a null pointer on failure.
Definition at line 63 of file directory.c.
References dir_open(), dir::inode, and inode_reopen().