Go to the source code of this file.
Macros | |
| #define | syscall0(NUMBER) |
| Invokes syscall NUMBER, passing no arguments, and returns the return value as an ‘int’. More... | |
| #define | syscall1(NUMBER, ARG0) |
| Invokes syscall NUMBER, passing argument ARG0, and returns the return value as an ‘int’. More... | |
| #define | syscall2(NUMBER, ARG0, ARG1) |
| Invokes syscall NUMBER, passing arguments ARG0 and ARG1, and returns the return value as an ‘int’. More... | |
| #define | syscall3(NUMBER, ARG0, ARG1, ARG2) |
| Invokes syscall NUMBER, passing arguments ARG0, ARG1, and ARG2, and returns the return value as an ‘int’. More... | |
Functions | |
| void | halt (void) |
| Projects 2 and later. More... | |
| void | exit (int status) |
| pid_t | exec (const char *file) |
| int | wait (pid_t pid) |
| bool | create (const char *file, unsigned initial_size) |
| bool | remove (const char *file) |
| int | open (const char *file) |
| int | filesize (int fd) |
| int | read (int fd, void *buffer, unsigned size) |
| int | write (int fd, const void *buffer, unsigned size) |
| void | seek (int fd, unsigned position) |
| unsigned | tell (int fd) |
| void | close (int fd) |
| mapid_t | mmap (int fd, void *addr) |
| Project 3 and optionally project 4. More... | |
| void | munmap (mapid_t mapid) |
| bool | chdir (const char *dir) |
| Project 4 only. More... | |
| bool | mkdir (const char *dir) |
| bool | readdir (int fd, char name[READDIR_MAX_LEN+1]) |
| bool | isdir (int fd) |
| int | inumber (int fd) |
| lib/user/syscall.h More... | |
Macro Definition Documentation
◆ syscall0
| #define syscall0 | ( | NUMBER | ) |
◆ syscall1
| #define syscall1 | ( | NUMBER, | |
| ARG0 | |||
| ) |
Invokes syscall NUMBER, passing argument ARG0, and returns the return value as an ‘int’.
◆ syscall2
| #define syscall2 | ( | NUMBER, | |
| ARG0, | |||
| ARG1 | |||
| ) |
Invokes syscall NUMBER, passing arguments ARG0 and ARG1, and returns the return value as an ‘int’.
◆ syscall3
| #define syscall3 | ( | NUMBER, | |
| ARG0, | |||
| ARG1, | |||
| ARG2 | |||
| ) |
Invokes syscall NUMBER, passing arguments ARG0, ARG1, and ARG2, and returns the return value as an ‘int’.
Function Documentation
◆ chdir()
| bool chdir | ( | const char * | dir | ) |
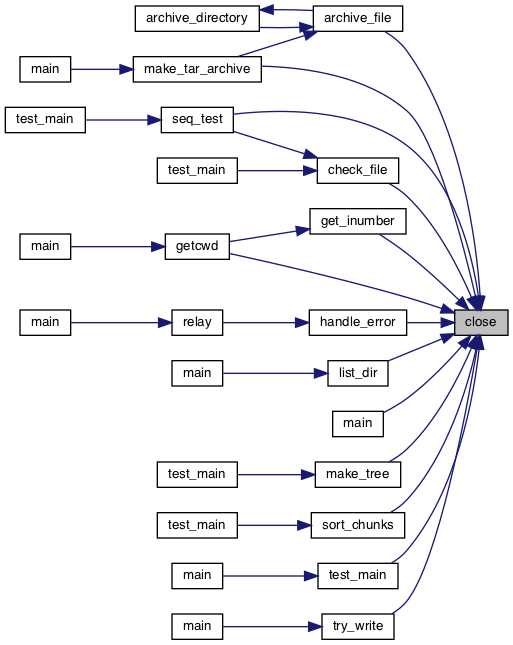
◆ close()
| void close | ( | int | fd | ) |
Definition at line 139 of file syscall.c.
References SYS_CLOSE, and syscall1.
Referenced by archive_file(), check_file(), get_inumber(), getcwd(), handle_error(), list_dir(), main(), make_tar_archive(), make_tree(), seq_test(), sort_chunks(), test_main(), and try_write().
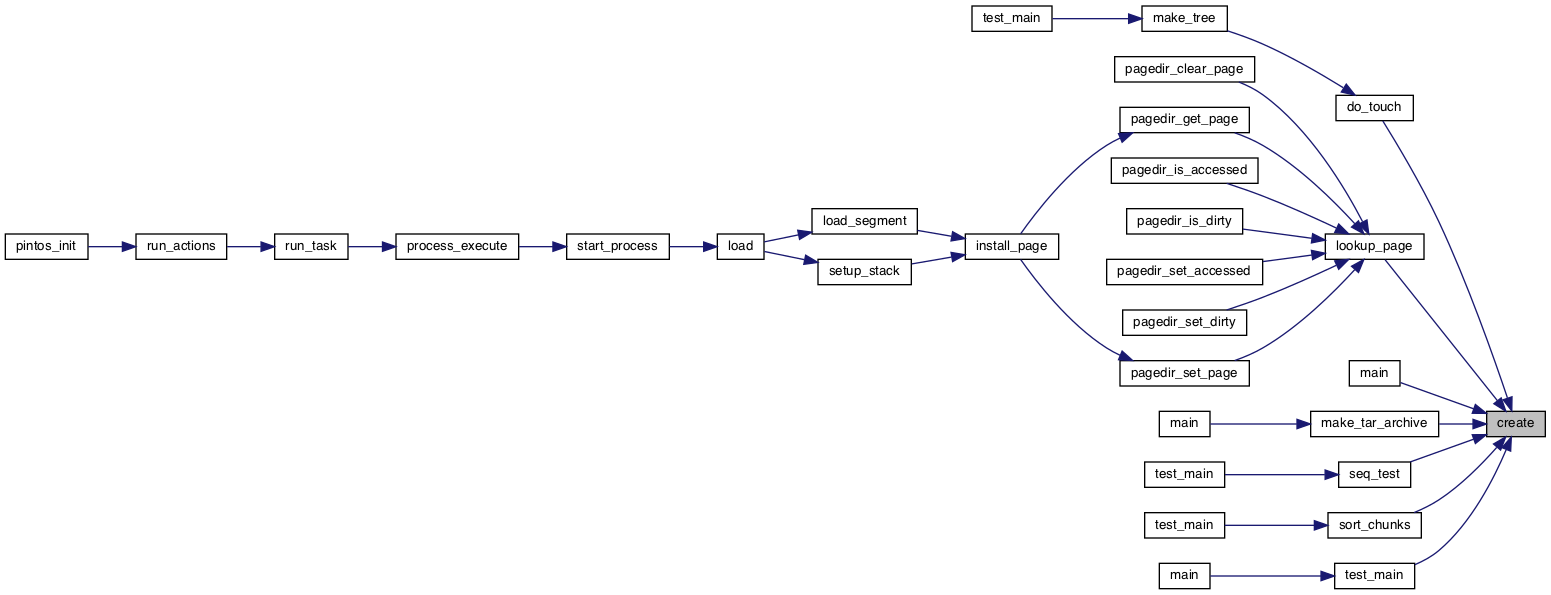
◆ create()
| bool create | ( | const char * | file, |
| unsigned | initial_size | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 91 of file syscall.c.
References SYS_CREATE, and syscall2.
Referenced by do_touch(), lookup_page(), main(), make_tar_archive(), seq_test(), sort_chunks(), and test_main().
◆ exec()
| pid_t exec | ( | const char * | file | ) |
Definition at line 79 of file syscall.c.
References SYS_EXEC, and syscall1.
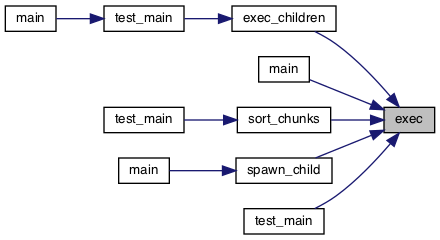
Referenced by exec_children(), main(), sort_chunks(), spawn_child(), and test_main().
◆ exit()
| void exit | ( | int | status | ) |
Definition at line 72 of file syscall.c.
References NOT_REACHED, SYS_EXIT, and syscall1.
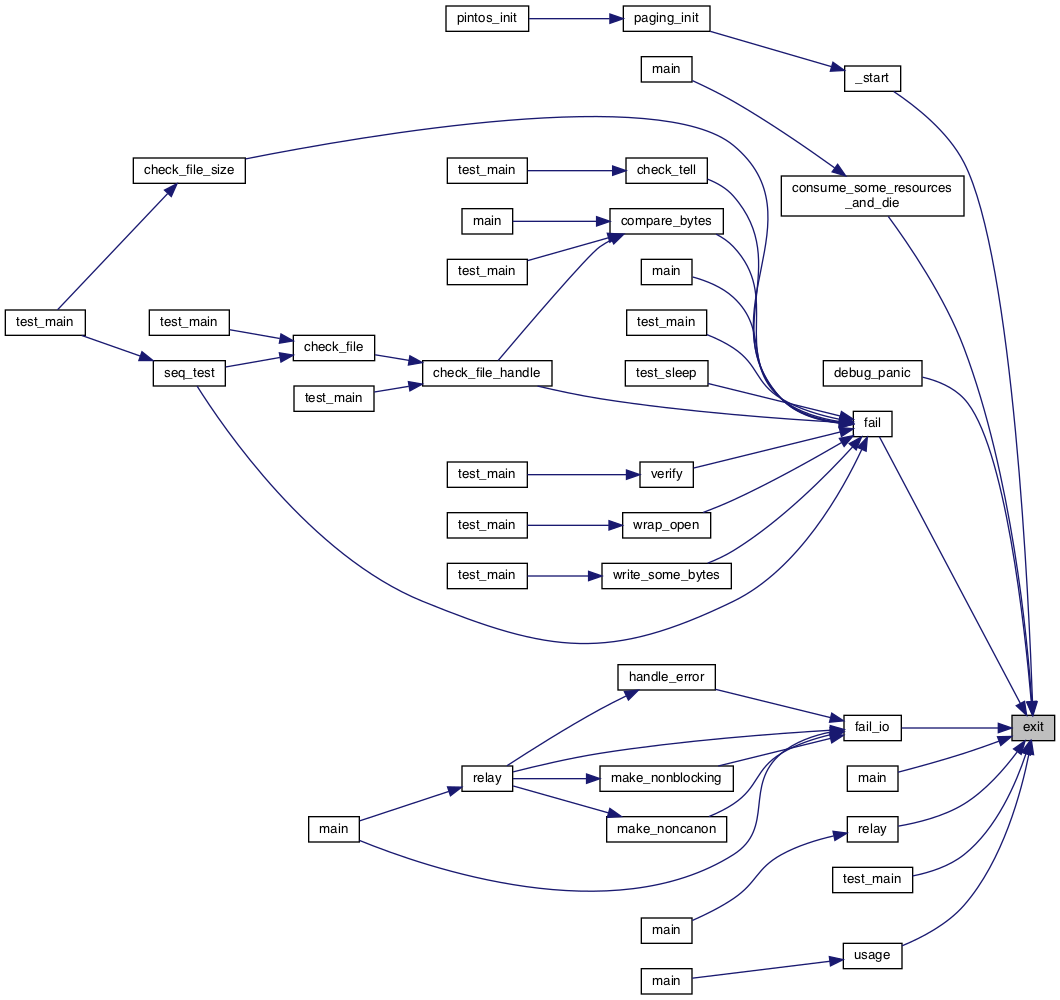
Referenced by _start(), consume_some_resources_and_die(), debug_panic(), fail(), fail_io(), main(), relay(), test_main(), and usage().
◆ filesize()
| int filesize | ( | int | fd | ) |
Definition at line 109 of file syscall.c.
References SYS_FILESIZE, and syscall1.
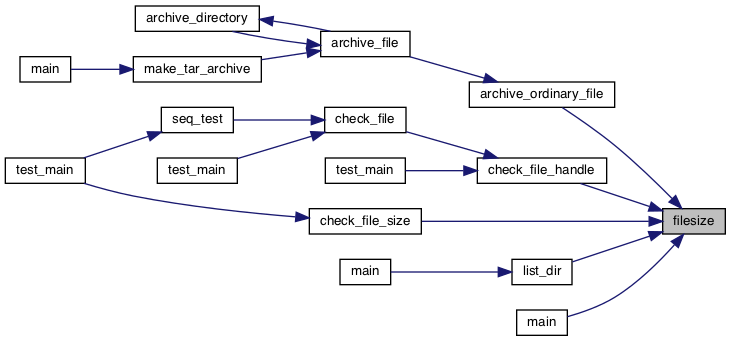
Referenced by archive_ordinary_file(), check_file_handle(), check_file_size(), list_dir(), and main().
◆ halt()
| void halt | ( | void | ) |
Projects 2 and later.
Definition at line 65 of file syscall.c.
References NOT_REACHED, SYS_HALT, and syscall0.
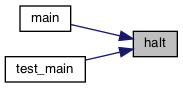
Referenced by main(), and test_main().
◆ inumber()
| int inumber | ( | int | fd | ) |
Definition at line 181 of file syscall.c.
References SYS_INUMBER, and syscall1.
Referenced by archive_file(), get_inumber(), getcwd(), list_dir(), and test_main().
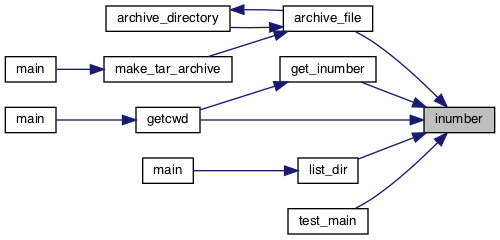
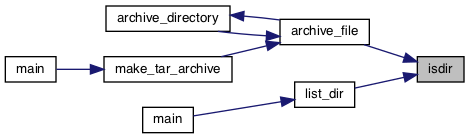
◆ isdir()
| bool isdir | ( | int | fd | ) |
Definition at line 175 of file syscall.c.
References SYS_ISDIR, and syscall1.
Referenced by archive_file(), and list_dir().
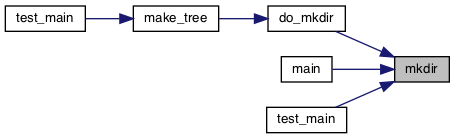
◆ mkdir()
| bool mkdir | ( | const char * | dir | ) |
Definition at line 163 of file syscall.c.
References SYS_MKDIR, and syscall1.
Referenced by do_mkdir(), main(), and test_main().
◆ mmap()
| mapid_t mmap | ( | int | fd, |
| void * | addr | ||
| ) |
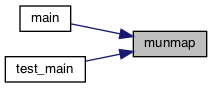
◆ munmap()
| void munmap | ( | mapid_t | mapid | ) |
Definition at line 151 of file syscall.c.
References SYS_MUNMAP, and syscall1.
Referenced by main(), and test_main().
◆ open()
| int open | ( | const char * | file | ) |
Definition at line 103 of file syscall.c.
References SYS_OPEN, and syscall1.
Referenced by archive_file(), check_file(), consume_some_resources(), consume_some_resources_and_die(), get_inumber(), getcwd(), list_dir(), main(), make_tar_archive(), make_tree(), remove_tree(), seq_test(), sort_chunks(), test_main(), try_write(), and wrap_open().
◆ read()
| int read | ( | int | fd, |
| void * | buffer, | ||
| unsigned | size | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 115 of file syscall.c.
References buffer, SYS_READ, and syscall3.
Referenced by archive_ordinary_file(), check_file_handle(), main(), read_line(), relay(), sort_chunks(), and test_main().
◆ readdir()
| bool readdir | ( | int | fd, |
| char | name[READDIR_MAX_LEN+1] | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 169 of file syscall.c.
References name, SYS_READDIR, and syscall2.
Referenced by archive_directory(), getcwd(), list_dir(), and test_main().
◆ remove()
| bool remove | ( | const char * | file | ) |
Definition at line 97 of file syscall.c.
References SYS_REMOVE, and syscall1.
Referenced by do_remove(), main(), and test_main().
◆ seek()
| void seek | ( | int | fd, |
| unsigned | position | ||
| ) |
◆ tell()
| unsigned tell | ( | int | fd | ) |
◆ wait()
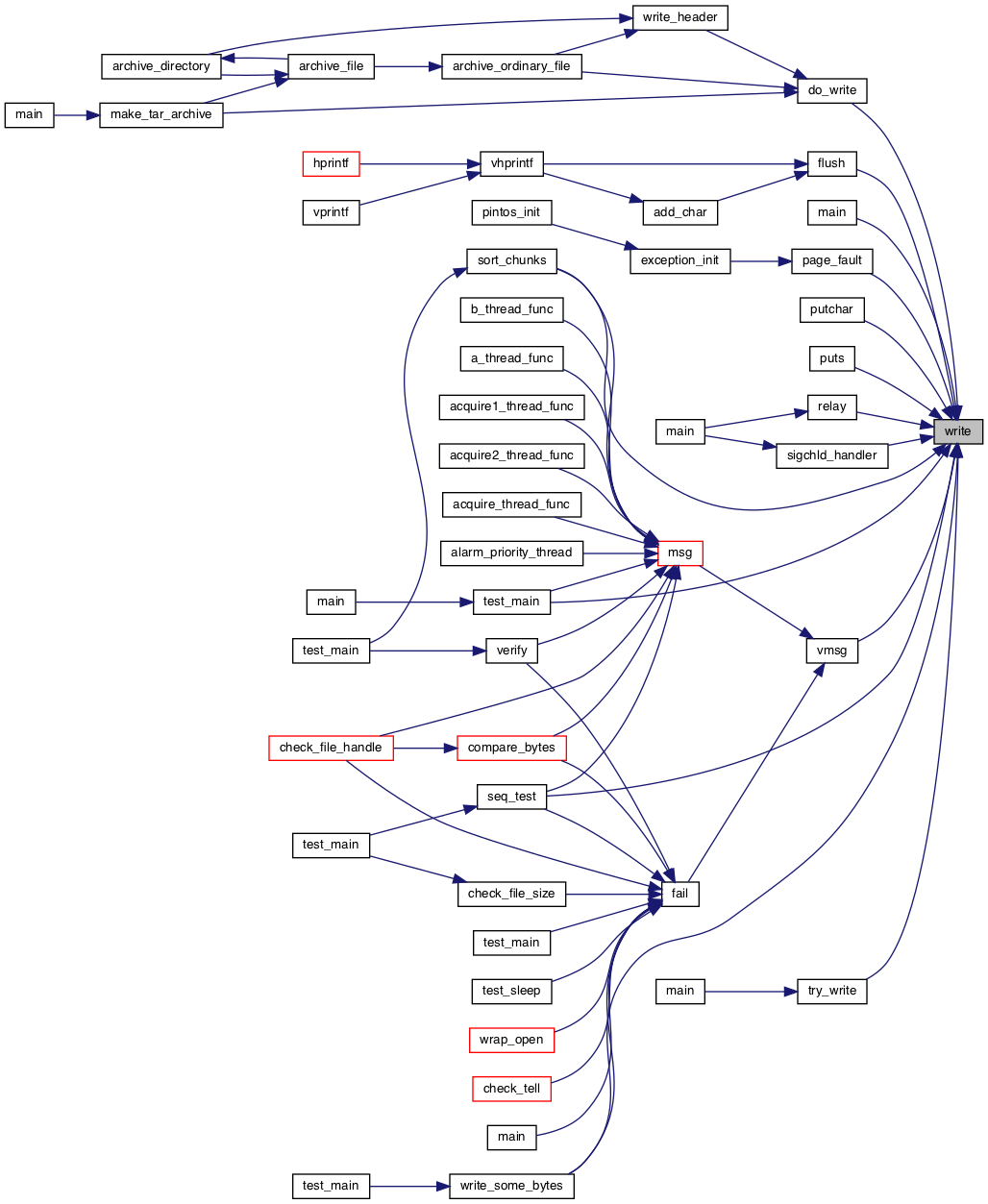
◆ write()
| int write | ( | int | fd, |
| const void * | buffer, | ||
| unsigned | size | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 121 of file syscall.c.
References buffer, SYS_WRITE, and syscall3.
Referenced by do_write(), flush(), main(), page_fault(), putchar(), puts(), relay(), seq_test(), sigchld_handler(), sort_chunks(), test_main(), try_write(), vmsg(), and write_some_bytes().