
Go to the source code of this file.
Data Structures | |
| struct | thread |
| A kernel thread or user process. More... | |
Macros | |
| #define | TID_ERROR ((tid_t) -1) |
| Error value for tid_t. More... | |
| #define | PRI_MIN 0 |
| Thread priorities. More... | |
| #define | PRI_DEFAULT 31 |
| Default priority. More... | |
| #define | PRI_MAX 63 |
| Highest priority. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef int | tid_t |
| Thread identifier type. More... | |
| typedef void | thread_func(void *aux) |
| typedef void | thread_action_func(struct thread *t, void *aux) |
| Performs some operation on thread t, given auxiliary data AUX. More... | |
Enumerations | |
| enum | thread_status { THREAD_RUNNING , THREAD_READY , THREAD_BLOCKED , THREAD_DYING } |
| States in a thread's life cycle. More... | |
Functions | |
| void | thread_init (void) |
| void | thread_start (void) |
| Starts preemptive thread scheduling by enabling interrupts. More... | |
| void | thread_tick (void) |
| Called by the timer interrupt handler at each timer tick. More... | |
| void | thread_print_stats (void) |
| Prints thread statistics. More... | |
| tid_t | thread_create (const char *name, int priority, thread_func *, void *) |
| Creates a new kernel thread named NAME with the given initial PRIORITY, which executes FUNCTION passing AUX as the argument, and adds it to the ready queue. More... | |
| void | thread_block (void) |
| Puts the current thread to sleep. More... | |
| void | thread_unblock (struct thread *) |
| Transitions a blocked thread T to the ready-to-run state. More... | |
| struct thread * | thread_current (void) |
| Returns the running thread. More... | |
| tid_t | thread_tid (void) |
| Returns the running thread's tid. More... | |
| const char * | thread_name (void) |
| Returns the name of the running thread. More... | |
| void | thread_exit (void) NO_RETURN |
| Deschedules the current thread and destroys it. More... | |
| void | thread_yield (void) |
| Yields the CPU. More... | |
| void | thread_foreach (thread_action_func *, void *) |
| Invoke function 'func' on all threads, passing along 'aux'. More... | |
| int | thread_get_priority (void) |
| Returns the current thread's priority. More... | |
| void | thread_set_priority (int) |
| Sets the current thread's priority to NEW_PRIORITY. More... | |
| int | thread_get_nice (void) |
| Returns the current thread's nice value. More... | |
| void | thread_set_nice (int) |
| int | thread_get_recent_cpu (void) |
| Returns 100 times the current thread's recent_cpu value. More... | |
| int | thread_get_load_avg (void) |
| threads/thread.h More... | |
Variables | |
| bool | thread_mlfqs |
| If false (default), use round-robin scheduler. More... | |
Macro Definition Documentation
◆ PRI_DEFAULT
◆ PRI_MAX
◆ PRI_MIN
◆ TID_ERROR
Typedef Documentation
◆ thread_action_func
| typedef void thread_action_func(struct thread *t, void *aux) |
◆ thread_func
◆ tid_t
| typedef int tid_t |
Enumeration Type Documentation
◆ thread_status
| enum thread_status |
Function Documentation
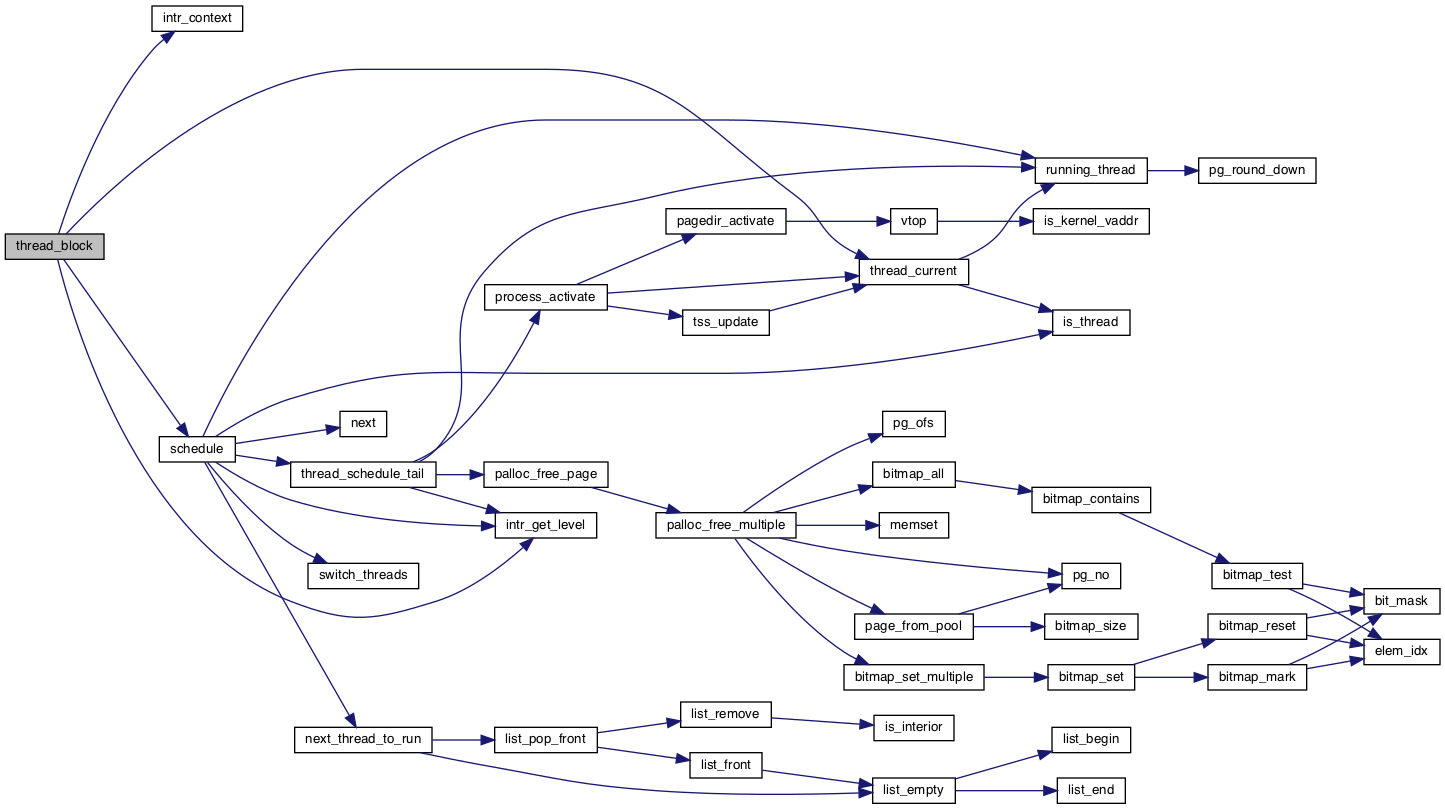
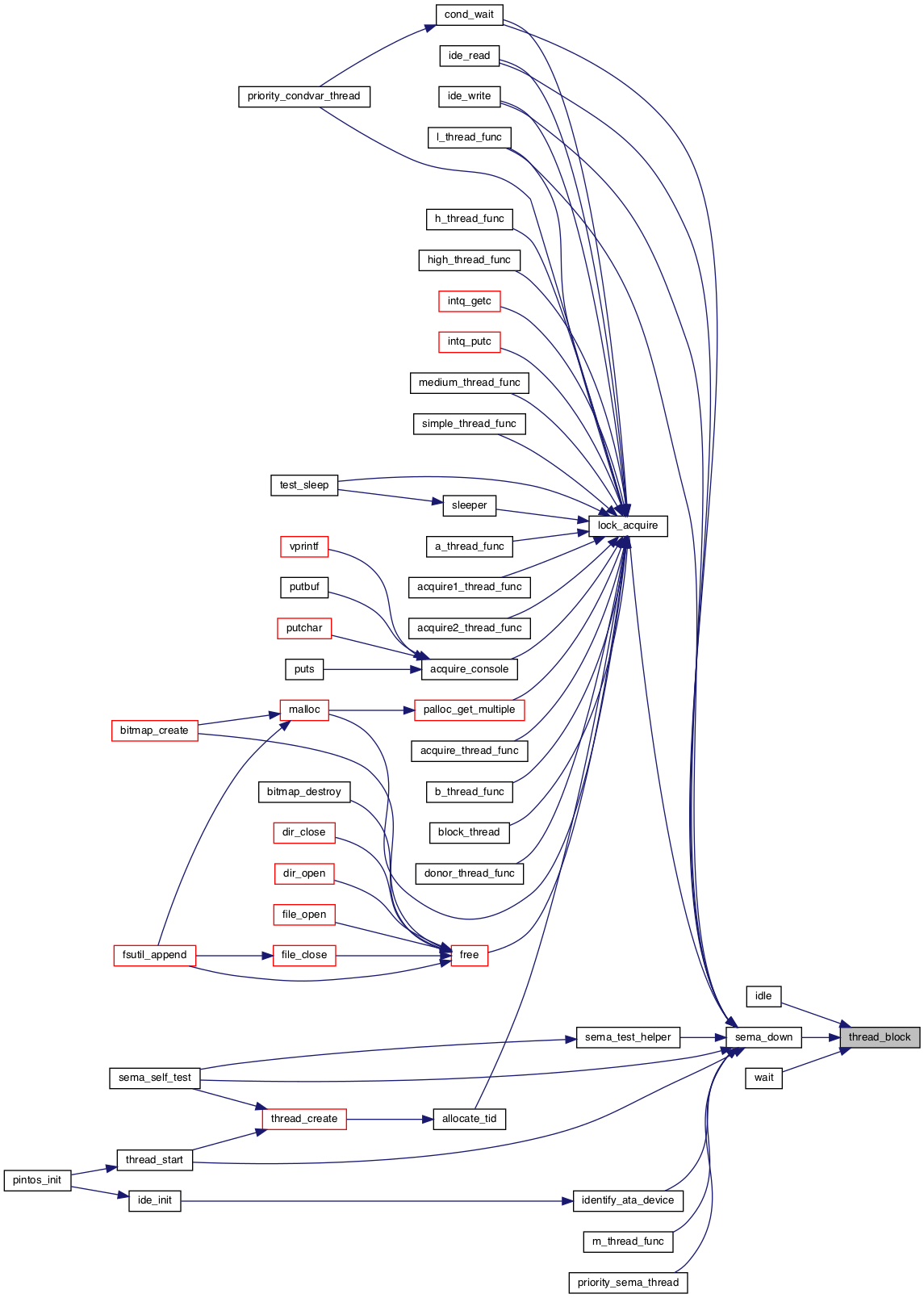
◆ thread_block()
| void thread_block | ( | void | ) |
Puts the current thread to sleep.
It will not be scheduled again until awoken by thread_unblock().
This function must be called with interrupts turned off. It is usually a better idea to use one of the synchronization primitives in synch.h.
Definition at line 214 of file thread.c.
References ASSERT, intr_context(), intr_get_level(), INTR_OFF, schedule(), thread::status, THREAD_BLOCKED, and thread_current().
Referenced by idle(), sema_down(), and wait().
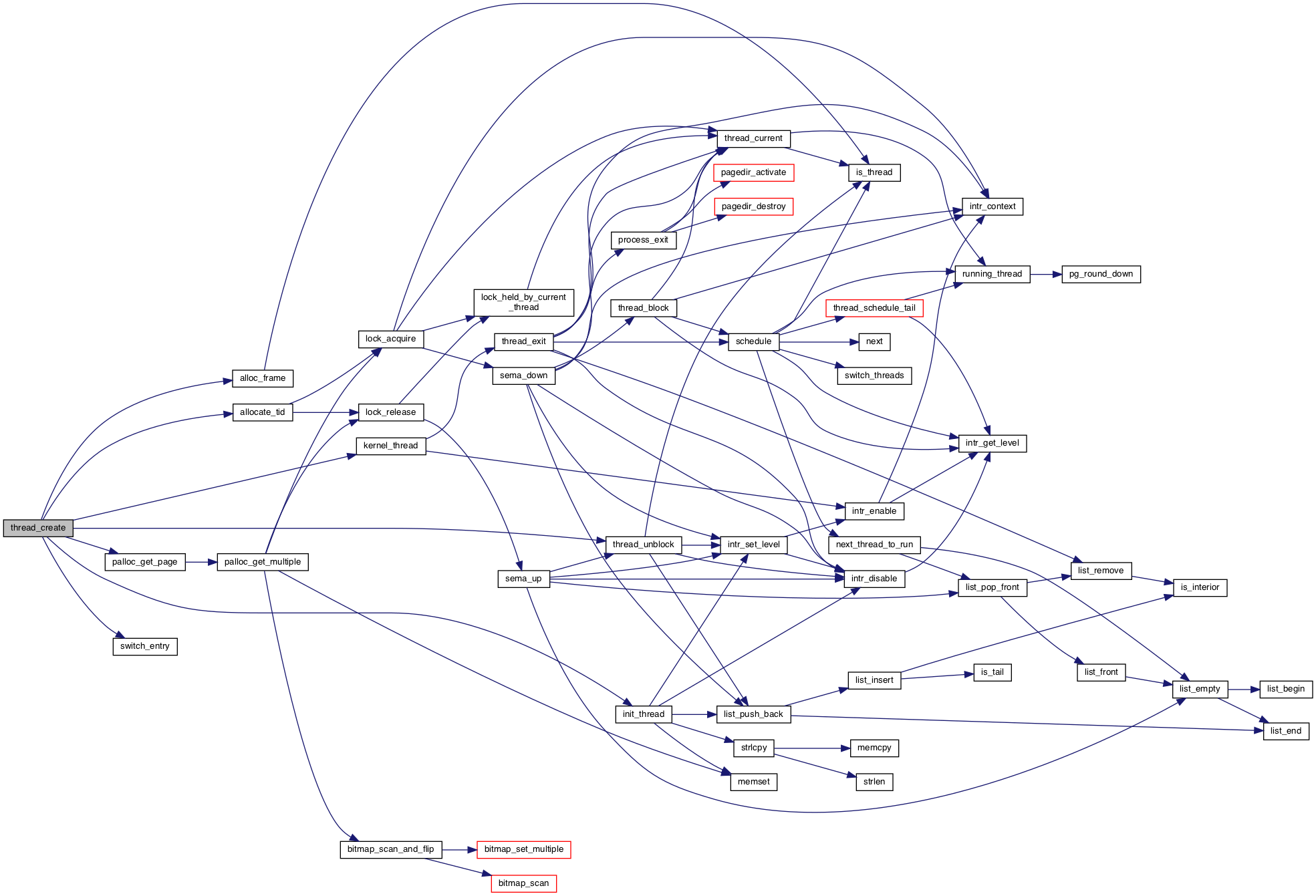
◆ thread_create()
| tid_t thread_create | ( | const char * | name, |
| int | priority, | ||
| thread_func * | function, | ||
| void * | aux | ||
| ) |
Creates a new kernel thread named NAME with the given initial PRIORITY, which executes FUNCTION passing AUX as the argument, and adds it to the ready queue.
Returns the thread identifier for the new thread, or TID_ERROR if creation fails.
If thread_start() has been called, then the new thread may be scheduled before thread_create() returns. It could even exit before thread_create() returns. Contrariwise, the original thread may run for any amount of time before the new thread is scheduled. Use a semaphore or some other form of synchronization if you need to ensure ordering.
The code provided sets the new thread's ‘priority’ member to PRIORITY, but no actual priority scheduling is implemented. Priority scheduling is the goal of Problem 1-3.
Definition at line 166 of file thread.c.
References alloc_frame(), allocate_tid(), ASSERT, kernel_thread_frame::aux, switch_threads_frame::ebp, switch_threads_frame::eip, switch_entry_frame::eip, kernel_thread_frame::eip, kernel_thread_frame::function, init_thread(), kernel_thread(), name, NULL, PAL_ZERO, palloc_get_page(), switch_entry(), thread_unblock(), thread::tid, and TID_ERROR.
Referenced by process_execute(), sema_self_test(), test_mlfqs_fair(), test_sleep(), and thread_start().
◆ thread_current()
| struct thread * thread_current | ( | void | ) |
Returns the running thread.
This is running_thread() plus a couple of sanity checks. See the big comment at the top of thread.h for details.
Definition at line 256 of file thread.c.
References ASSERT, is_thread(), running_thread(), thread::status, and THREAD_RUNNING.
Referenced by idle(), install_page(), load(), lock_acquire(), lock_held_by_current_thread(), lock_try_acquire(), print_stacktrace(), process_activate(), process_exit(), sema_down(), thread_block(), thread_exit(), thread_get_priority(), thread_name(), thread_set_priority(), thread_tick(), thread_tid(), thread_yield(), tss_update(), and wait().
◆ thread_exit()
| void thread_exit | ( | void | ) |
Deschedules the current thread and destroys it.
Never returns to the caller.
Definition at line 281 of file thread.c.
References thread::allelem, ASSERT, intr_context(), intr_disable(), list_remove(), NOT_REACHED, process_exit(), schedule(), thread::status, thread_current(), and THREAD_DYING.
Referenced by kernel_thread(), kill(), pintos_init(), start_process(), and syscall_handler().
◆ thread_foreach()
| void thread_foreach | ( | thread_action_func * | func, |
| void * | aux | ||
| ) |
Invoke function 'func' on all threads, passing along 'aux'.
This function must be called with interrupts off.
Definition at line 320 of file thread.c.
References all_list, thread::allelem, ASSERT, intr_get_level(), INTR_OFF, list_begin(), list_end(), list_entry, and list_next().
Referenced by debug_backtrace_all().
◆ thread_get_load_avg()
| int thread_get_load_avg | ( | void | ) |
◆ thread_get_nice()
| int thread_get_nice | ( | void | ) |
◆ thread_get_priority()
| int thread_get_priority | ( | void | ) |
Returns the current thread's priority.
Definition at line 343 of file thread.c.
References thread::priority, and thread_current().
Referenced by donor_thread_func(), and medium_thread_func().
◆ thread_get_recent_cpu()
| int thread_get_recent_cpu | ( | void | ) |
◆ thread_init()
| void thread_init | ( | void | ) |
◆ thread_name()
| const char * thread_name | ( | void | ) |
Returns the name of the running thread.
Definition at line 247 of file thread.c.
References thread::name, and thread_current().
Referenced by alarm_priority_thread(), donor_thread_func(), interloper_thread_func(), kill(), priority_condvar_thread(), priority_sema_thread(), and simple_thread_func().
◆ thread_print_stats()
| void thread_print_stats | ( | void | ) |
Prints thread statistics.
Definition at line 144 of file thread.c.
References idle_ticks, kernel_ticks, printf(), and user_ticks.
Referenced by print_stats().
◆ thread_set_nice()
| void thread_set_nice | ( | int | ) |
◆ thread_set_priority()
| void thread_set_priority | ( | int | new_priority | ) |
Sets the current thread's priority to NEW_PRIORITY.
Definition at line 336 of file thread.c.
References thread::priority, and thread_current().
Referenced by changing_thread().

◆ thread_start()
| void thread_start | ( | void | ) |
Starts preemptive thread scheduling by enabling interrupts.
Also creates the idle thread.
Definition at line 106 of file thread.c.
References idle(), intr_enable(), PRI_MIN, sema_down(), sema_init(), and thread_create().
Referenced by pintos_init().

◆ thread_tick()
| void thread_tick | ( | void | ) |
Called by the timer interrupt handler at each timer tick.
Thus, this function runs in an external interrupt context.
Definition at line 123 of file thread.c.
References idle_thread, idle_ticks, intr_yield_on_return(), kernel_ticks, NULL, thread_current(), thread_ticks, TIME_SLICE, and user_ticks.
Referenced by timer_interrupt().
◆ thread_tid()
| tid_t thread_tid | ( | void | ) |
Returns the running thread's tid.
Definition at line 273 of file thread.c.
References thread_current(), and thread::tid.
◆ thread_unblock()
| void thread_unblock | ( | struct thread * | t | ) |
Transitions a blocked thread T to the ready-to-run state.
This is an error if T is not blocked. (Use thread_yield() to make the running thread ready.)
This function does not preempt the running thread. This can be important: if the caller had disabled interrupts itself, it may expect that it can atomically unblock a thread and update other data.
Definition at line 232 of file thread.c.
References ASSERT, thread::elem, intr_disable(), intr_set_level(), is_thread(), list_push_back(), ready_list, thread::status, THREAD_BLOCKED, and THREAD_READY.
Referenced by sema_up(), signal(), and thread_create().
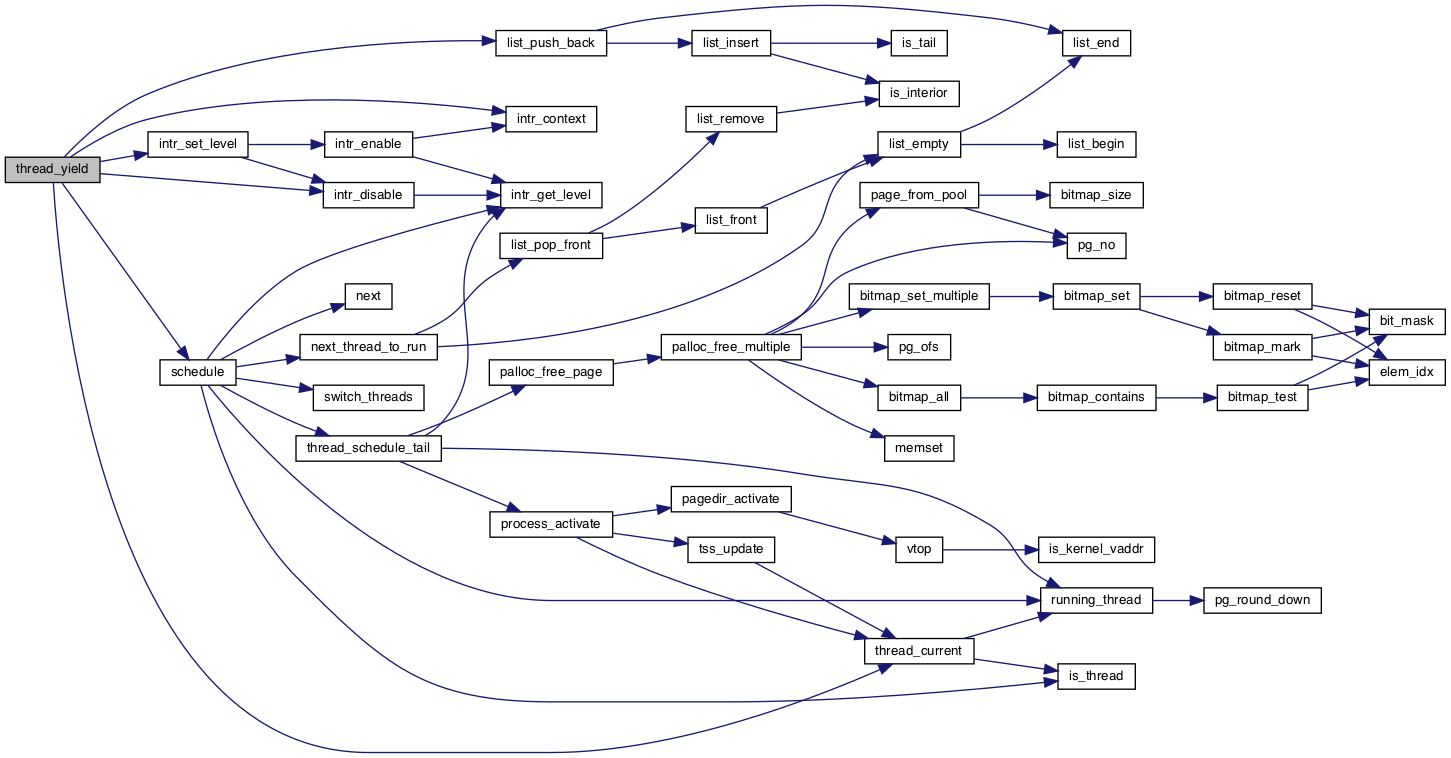
◆ thread_yield()
| void thread_yield | ( | void | ) |
Yields the CPU.
The current thread is not put to sleep and may be scheduled again immediately at the scheduler's whim.
Definition at line 302 of file thread.c.
References ASSERT, thread::elem, idle_thread, intr_context(), intr_disable(), intr_set_level(), list_push_back(), ready_list, schedule(), thread::status, thread_current(), and THREAD_READY.
Referenced by intr_handler(), medium_thread_func(), simple_thread_func(), sleeper(), and timer_sleep().
Variable Documentation
◆ thread_mlfqs
|
extern |
If false (default), use round-robin scheduler.
If true, use multi-level feedback queue scheduler. Controlled by kernel command-line option "-o mlfqs".
Definition at line 60 of file thread.c.
Referenced by parse_options(), test_mlfqs_fair(), and test_sleep().
